If you have had a lump or bump behind your ear lobe, what did it mean? Commonly, this kind of condition is left to observation and is not regarded as an emergency or a serious problem. It may not be true given the seriousness some of the differentials could mean.
Infections are regarded as serious problems and when it comes to the ear, which has bones and cartilages along its canal and with regard to its proximity to the brain, you will need immediate interventions.
There are many causes which will be discussed in this material linked to formation of lumps of bumps behind the ear lobe. Treatment will depend on a right diagnosis in connection to their morphology and histology. You will notice that the lumps in question could range from small to really large such as in keloidal swellings.
Causes & Meaning
Some of the causes of lumps or bumps behind your ear lobe are discussed in this section. Their types are determined by the causes and so will their characteristics.
Mastoid bone infection
The bone that is located at the hind of the ear is known as the mastoid. The infection that therefore arises from this bone is mastoiditis making it a clinically significant condition that requires immediate attention.
Your doctor will diagnose you with mastoiditis based on the presence of a bump behind the ear which may be a pus-filled cyst on the visible on the skin.
Antibiotics should be able to rehabilitate your ear and save it from further bone damage but at times a minor surgery will be proposed.
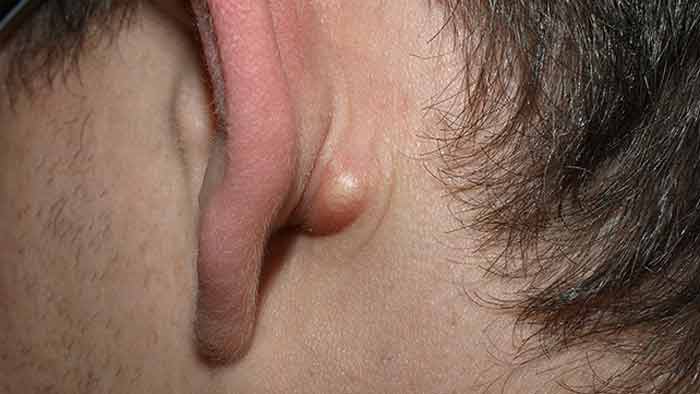
Sebaceous cysts
These are cysts that form on the sebaceous glands. Since these glands are everywhere, then, the cysts can form anywhere. The hind of the ear is one probable location.
These growths will be characterized by a sac filled with sebum which has a yellowish resemblance to pus.
Unlike the infected bone, mastoiditis, sebaceous cysts are painless bumps and are considered relatively less harmful. This is not to say that they are cancerous however and despite this subtleness, they are quite discomforting due to their large sizes.
Lymphadenitis
There are lymph nodes behind the ear known as the posterior articular lymph nodes. Lymphadenitis is a known lymphadenopathy in which the latter term refers to a disease condition of the lymph gland.
When the hind of the ear is palpated, you will be able to feel hard balls that are mobile. Due to their mobility, you can almost not have a grip of them. Such inflammations of the lymph nodes are caused by infections that could either be bacterial or viral.
Hemophilus influenza among other pathogens such as Streptococcus pyogenes, a common cause of tonsillitis are the biggest culprits.
Viral infections such as chicken pox (Varicella zoster virus), measles, mumps rubella, cytomegalovirus (CMV)and mononucleosis, commonly referred to as the ‘kissing disease’ or glandular fever presents with swollen balls behind the ear.
They are painful when touched (tender). The good thing is that to diagnose such infections, you will need to consider accompanying symptoms such as those that are systemic including fever, fatigue, a sore throat, pain around the eyes and ears too.
HIV/AIDs has some of these infectious agents as causes of its opportunistic infections.
Benign tumor
tumors are swellings that can be non-cancerous, precancerous or cancerous. Cancerous tumors can either be benign or malignant.
When tumors are benign, they haven’t metastasized meaning that the abnormal growth of cells is localized and the otherwise goes to malignant.
If you have a swelling or a lump behind the ear, a benign tumor could be probable. They are characterized by painless and usually harmless small balls or nodules.
When palpated upon, they feel is similar to that when palpating the lymph nodes. The position of the tumor is however different and can be felt on the scalp, ear canal and behind the ear. One such tumor is the cholesteatoma normally associated with mobility, and some systemic symptoms such as dizziness.
Cancer
You may notice some painless bumps behind your ear that are getting bigger and bigger. Cancer of the ear affects the lymph nodes making them swell and this could be palpated for its feel.
However, the tumor outgrows the nodes to an extent that the salivary glands are affected. According to the Cancer Research Center of United Kingdom, the lumps are pink in color, have a scaly surface that is hard, may bleed easily, can ulcerate and can appear as growing moles behind the ear.
Piercing
If you have got a piercing on the cartilage of the ear lobe/pinna that gets infected, an inflammation could occur.
There are bacterial infections such as Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomnas aeruginosa that are mostly associated with such infections and could turn them into more complicated infections.
This therefore raises the need for routinely cleaning the ear piercing with some surgical spirit to rid the ear of disease causing pathogens.
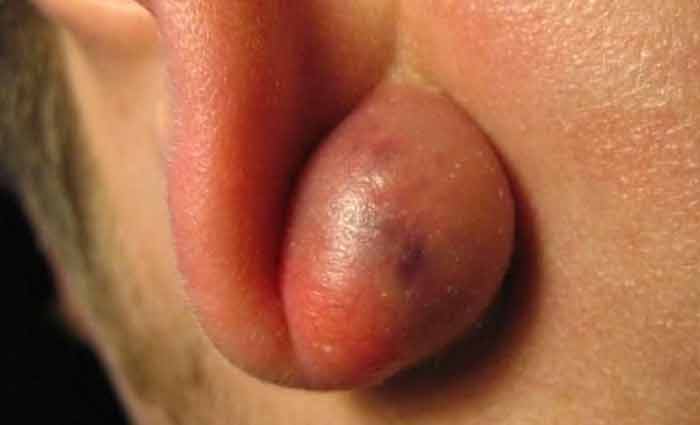
Lipoma
Another mobile bump on palpation could be a lipoma, fatty bumps behind the ear and under the skin. The nodule formed is easily noticeable and are voted the most common non-cancerous growths.
Tempormandibular disorders (TMDs):
Such includes temporomandibular jaw which manifests as a bump along and below the jaw line on the neck and behind the ear.
This problem is presumed to occur with the jaw muscles and the joint of the jaw itself. It is painful and the arising inflammation is what is responsible for the visible lump you will have.
Insect bites or stings
You can never overestimate the possibility of having a bite as part of the diagnosis and this will come out as the doctor takes your history of presenting illness.
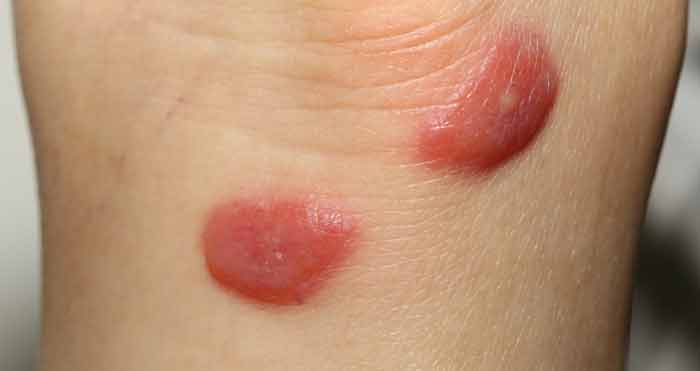
Some of the insects that could bite you are whose bites are potentially dangerous are wasps, bees and spiders. In order to have this as an option, the swelling has an immediate onset, will be localized and will probably go away on its own.
Wearing glasses
When your glasses are not well fitting or tightly fitting, they could make your sweat on the nose and the back of the ears. When these pores are clogged, they could form a whitehead or an infected cyst. There may be a rash or pimple on the nose bridge too.
There are other causes of lumps behind your ears including psoriasis, acne, hormonal imbalances, stress, blood blisters and ingrown hairs/folliculitis.
What does it indicate when the bump
Small & Large
Sizes determined the cause and could be a lead to a proper diagnosis. For instance, when the lump is small, it could mean that perhaps you have a zit, acne, rash, insect bite, hormonal imbalance or folliculitis. Basically, small bumps are not so worrisome.
Large bumps or lumps are indicative of tumors, either benign or cancerous, infections of the skin and lymphadenopathies. These are relatively more serious conditions.
Painful
Other than making an uncalled-for appearance behind the ear, some bumps and lumps could be really painful. Infections are painful in a way that could either be achy or tender.
Most of these bumps are linked to some systemic signs too such as fatigue, fevers and headaches. Blind pimples or what is commonly known as closed comedones are painful and are seen in those who have acne. When they turn into blackheads or open comedones, they are less painful or painless.
Hard
Hard lumps behind the ear are characteristic of pilomatricomas, lipomas, cholesteatomas, among other benign tumors that can appear behind the ear. Pilomatricomas are benign tumors that form when there is calcification in the matrix of the hair. They normally start as small bumps then grow progressively into larger ones (WebMD).
It is on the bone
When the lump or bump is on the bone and painful, then it could be an infection of the mastoid bone, mastoiditis. This condition is a serious complication of the inflammation of the middle section of the ear.
There will be swelling and tenderness of the skin especially behind the ear alongside redness, fever and discharge from the ear. During treatment with antibiotics, the pus needs to be drained as well as the lining and the bone infected removed from the mastoid.
It is red
Redness is a cardinal sign of inflammation. Dermatitis, which is an inflammation, especially the seborrheic dermatitis can occur behind the ears. This is characterized by formation of scales and pimples of this color.
Weird and hard
Swelling behind the ear is in itself weird. When it is hard, it could be a growth in the skin such as tumor. Some of the tumors mentioned before in this material are pilomatricomas, lipomas and cholesteatomas. Mastoiditis is an infection that results in a hard bump too.
Swollen
This could be any of the causes of bumps and lumps behind the ear apart from the tumorous growths mentioned. It could be that the lymph nodes are swollen, bases of follicles swollen in folliculitis or sebaceous cysts.
Swelling is a form of hypertrophy which means that the cells abnormally increase in size but not in number. Hyperplasia, an increase in the number and population of cells, abnormally, is what leads to a tumor.
Itchy
Allergies and some infections could cause itchiness. Itchiness could come about as an undesirable effect of healing when fibrin is deposited to form a clot. Dermatitis is the biggest culprit and so are insect bites.
Treatment
Treatment of lumps behind the ears is dependent on the cause. When the diagnosis has been made, then a treatment plan and schedule can be developed. Here are some of the treatment options against the causes discussed in this article.
Mastoid bone infection:
for this, you will require antibiotics. The antibiotics in this case are administered intravenously. If there is not improvement after this IV administration, then surgical treatment is instituted.
This involves draining of the pus and removal of infected lining of the ear canal together with the infected bone tissue. Analgesics are administered so as to reduce the inflammation and alleviate the pain.
Sebaceous cysts:
For these, if the cause of the cysts is Gardner syndrome, s subtype of familial adenomatous polyposis, then treatment may be management of the presenting signs. Therefore, the main problem may not be addressed.
Tea tree oil and glycolic acid can be used as options. When using tea tree oil, dilute the oil with an equal part of warm water then dip a cotton ball into the solution until it is saturated.
Apply onto the hind of the ear where there is a cyst then leave to stand for 5 minutes before washing off with some soap.
Glycolic acid is a scrub that helps exfoliate the skin and help sebum properly excreted. Mix 5 teaspoonfuls of white sugar then add some olive oil. Apply to the cyst while rubbing gently in a circular motion before rising 5 minutes later. Do this after every two days for the first week.
Lymphadenitis
since viral infections are the most common cause, and yet viral infections have to take their course, management of the signs and symptoms is preferred.
This involves taking enough fluids (hydrating), taking analgesics for the fever and myalgia, taking antibacterial for any secondary infection and enough bed rest. Within 5-10 days, the infection is expected to have resolved allowing you to continue your normal routine.
Benign tumor and cancers
These two will require surgical removal of the tumor cells. Observational or watchful waiting with scheduled diagnoses will be preferred so as to ensure that the tumor is not malignant. However, there are anticancer agents that can be taken depending on the cancer diagnosed.
Piercing infections
Treatment is done through intake of antibiotics and analgesics. It is advised that you ensure that you clean the ear piercing with surgical spirit every day. This involves using a clean cotton wool dipped in some of the spirit then rubbing it in your ear.
Tempormandibular disorders (TMDs)
This condition has not been well elucidated. However, the doctor may prescribe analgesics for the inflammation and pain alongside some physiotherapy.
Insect bites or stings
Anti-allergy medications including anti-histamines are administered for this. Such include cetirizine, loratidine or chlopheniramine.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are also administered as topical formulations so as to reduce the swelling.
Swelling from wearing glasses
You need to select a pair of glasses that are properly and comfortably fitting.